Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yonaga, Yusuke; Yoshikawa, Kiyotaka*; Shimada, Koji
JAEA-Testing 2020-002, 19 Pages, 2020/05
Rock thin sections are used for instrument analyses such as EPMA, LA-ICP-MS as well as microstructural observations by optical microscope. Fabrication of thin section, reported here, is one of the fundamental techniques in classical and state-of-the-art geological research. This report provides not only general procedure but also some ingenuity, precautions and equipment maintenance with visual exemplification for first-time or inexperienced users in the Tono Geoscience Center.
Tamura, Koji*; Toyama, Shinichi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 61(5), p.413 - 415, 2019/05
, 61(5), p.413 - 415, 2019/05
In decommissioning of nuclear reactors, it is necessary to disassemble the nuclear reactor structure. In addition to the conventional cutting method, the laser method has many advantages such as remote controllability and no need for replacement parts such as blades, which can be a powerful choice. Nuclear reactor structure such as a pressure vessel are made of steel materials with a thickness exceeding 100 mm, and the laser method has poor knowledge and experience in cutting such thick steel materials. Therefore, as a result of trial cutting of steel materials under various cutting conditions with the high power fiber laser which is progressively available nowadays, it has been demonstrated that laser cutting is also possible for thick plates such as those used in nuclear reactors, and cutting of thick steel plates. We also developed the cutting technology using remote control using a robot in order to apply it to the decommissioning of thick steel cutting on the spot.
Inagawa, Hirofumi*
Ebara Jiho, (257), P. 38, 2019/04
no abstracts in English
Abe, Yuta; Nakagiri, Toshio; Watatani, Satoshi*; Maruyama, Shinichiro*
JAEA-Technology 2017-023, 46 Pages, 2017/10
This is a report on Abrasive Water Jet (AWJ) cutting work carried out on specimen, which was used for Simulated Fuel Assembly Heating Examination by Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS) molten core behavior analysis group in February 2016. The simulated fuel assembly is composed of Zirconia for the outer crucible/simulated fuel, stainless steel for the control blade and Zircaloy (Zr) for the cladding tube/channel box. Therefore, it is necessary to cut at once substances having a wide range of fracture toughness and hardness. Moreover, it is a large specimen with an approximate size of 300 mm. In addition, epoxy resin has high stickiness, making it more difficult to cut. Considering these effects, AWJ cutting was selected. The following two points were devised, and this specimen could be cut with AWJ. If it was not possible to cut at one time like a molten portion of boride, it was repeatedly cut. By using Abrasive Suspension Jet (ASJ) system with higher cutting ability than Abrasive Injection Jet (AIJ, conventional method) system, cutting time was shortened. As a result of this work, the cutting method in Simulated Fuel Assembly Heating Examination was established. Incidentally, in the cutting operation, when the cutting ability was lost at the tip of the AWJ, a curved cut surface, which occurs when the jet flowed away from the feeding direction, could be confirmed at the center of the test body. From the next work, to improve the cutting efficiency, we propose adding a mechanism such as turning the cutting member itself for re-cutting from the exit side of the jet and appropriate traverse speed to protect cut surface.
Maruyama, Shinichiro*; Watatani, Satoshi*
Mitsui Sumitomo Kensetsu Gijutsu Kenkyu Kaihatsu Hokoku, (15), p.107 - 112, 2017/10
It is essential to estimate characteristics and forms of fuel debris for safe and reliable removing at the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F). For the estimation, melting behavior of fuel assembly in the accident is being researched. To proceed the research, the fuel debris were need to cut, and the abrasive water jet (AWJ) which had enough results for cutting ceramic material or mixed material of zirconium alloy and stainless. The test results demonstrated that AWJ could cut the fuel assembly and accumulated the cutting data which will be subservient when removing the fuel debris in future.
Toyama, Shinichi; Minehara, Eisuke*
Dekomisshoningu Giho, (56), p.55 - 65, 2017/09
Development of the steel cutting technology which employs high power fiber laser for the industrial applicability of the laser technology has been carried out at The Wakasa Wan Energy Research Center (WERC). At present, the laser technologies for dismantling and decontamination are concurrently being developed to the application measure of nuclear dismantling for domestic nuclear power plants in the future. Dismantling of nuclear facilities is now under the development in the world. The necessity of the technology is increasing and the development is strongly expected. Beside the relative easiness to handle compared with other laser system, suppression of production of secondary radioactive waste and dose exposure can be realized by the dramatic improvement by excelled thermal density of fiber laser. This paper provides recent results from cutting technology for thick steels aiming disassembling nuclear pressure vessel, and decontamination machine technology which works under high radiation dose, explaining the results from cutting experiment of steels and the actual equipment and from the radiation resistance experiment for component devices.
Tezuka, Masashi; Nakamura, Yasuyuki; Iwai, Hiroki; Sano, Kazuya
JAEA-Technology 2015-047, 114 Pages, 2016/03
It was reported that Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant had been lost the function of cooling the reactor by the Tohoku Earthquake. It is assumed that the original shapes of the internal core are not kept and the inside of the reactor makes so narrow in the space, however the fuel debris and the molten internal core will have to be removed for the decommissioning of 1F. We concerned the suppression of dross by optimization of cutting conditions, in using some moderated test pieces. And we can improve the cutting capability by heating the objects in advance. Moreover, it's possible that plasma arc cutting can cut off the mixed material the fuel debris and the molten internal core by using the cooperation cutting technique both the plasma arc and the plasma jet cutting. From these results, we have got the prospect that plasma cutting method can apply the removal of the fuel debris and the molten internal core.
Nakamura, Yasuyuki; Iwai, Hiroki; Mizui, Hiroyuki; Sano, Kazuya
JAEA-Technology 2015-045, 137 Pages, 2016/03
FUGEN is 9 m outer-diameter and 7m height, and characterized by its tube-cluster construction that contains 224 fuel channels arranging both the pressure and the calandria tubes coaxially in each channel. And the periphery part of the core has the laminated structure composed of up to 150 mm thickness of carbon steel for radiation shielding. The structure of the reactor, which is made of various materials such as stainless steel, carbon steel, zirconium alloy and aluminum. The reactor is planning to be dismantled under water in order to shield the radiation ray around the core and prevent airborne dust generated by the cutting, the temporary pool structure and the remote-operated dismantling machines needs to be installed on the top of reactor. In consideration of above the structure of Fugen reactor, the cutting method was selected for dismantling the reactor core in order to shorten the dismantling term and reduce the secondary waste.
Takahashi, Akihisa*; Kubo, Makoto*; Ma, H.*; Nakagawa, Akiko*; Yoshida, Yukari*; Isono, Mayu*; Kanai, Tatsuaki*; Ono, Tatsuya*; Furusawa, Yoshiya*; Funayama, Tomoo; et al.
Radiation Research, 182(3), p.338 - 344, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:57 Percentile:90.66(Biology)To clarify whether high-LET radiation inhibits all repair pathways or specifically one repair pathway, studies were designed to examine the effects of radiation with different LET values on DNA DSB repair and radiosensitivity. Embryonic fibroblasts bearing repair gene KO were exposed to X rays, carbon-, iron-, neon- and argon-ion beams. Cell survival was measured with colony-forming assays. The sensitization enhancement ratio (SER) values were calculated using the 10% survival dose of wild-type cells and repair-deficient cells. Cellular radiosensitivity was listed in descending order: double-KO cells  NHEJ-KO cells
NHEJ-KO cells  HR-KO cells
HR-KO cells  wild-type cells. Although HR-KO cells had an almost constant SER value, NHEJ-KO cells showed a high-SER value when compared to HR-KO cells, even with increasing LET values. These results suggest that with carbon-ion therapy, targeting NHEJ repair yields higher radiosensitivity than targeting homologous recombination repair.
wild-type cells. Although HR-KO cells had an almost constant SER value, NHEJ-KO cells showed a high-SER value when compared to HR-KO cells, even with increasing LET values. These results suggest that with carbon-ion therapy, targeting NHEJ repair yields higher radiosensitivity than targeting homologous recombination repair.

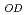 state
stateAkagi, Hiroshi; Fukazawa, Hiroshi; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yokoyama, Atsushi
Journal of Chemical Physics, 123(18), p.184305_1 - 184305_7, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:57.25(Chemistry, Physical)Vibrationally excited HOD in the fourth overtone state of the OD-stretching mode (5
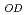 ) has been photodissociated by ultraviolet photolysis at ca. 243.1 nm. Branching ratio between the OH- and OD-bond dissociation channels has been determined by detecting the H and D atoms. The OD-bond dissociation is the dominant channel, with the yield of H atom generated by the photolysis being below the detection limit.
) has been photodissociated by ultraviolet photolysis at ca. 243.1 nm. Branching ratio between the OH- and OD-bond dissociation channels has been determined by detecting the H and D atoms. The OD-bond dissociation is the dominant channel, with the yield of H atom generated by the photolysis being below the detection limit.
 rays
raysYokota, Yuichiro; Shikazono, Naoya; Tanaka, Atsushi; Hase, Yoshihiro; Funayama, Tomoo; Wada, Seiichi; Inoue, Masayoshi*
Radiation Research, 163(5), p.520 - 525, 2005/05
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:48.84(Biology)Higher plants are generally more tolerant to ionizing radiation than mammals. To explore the radiation tolerance of higher plants, the amount of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) induced by  -rays was investigated in tobacco BY-2 cells and compared with that investigated in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO)-K1 cells as a reference. The resulting DNA fragments were separated by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and stained with SYBR Green I. Initial DSB yield was then quantified from the fraction of DNA fragments shorter than 1.6 Mbp based on the assumption of random distribution of DSBs. The DSB yield in tobacco BY-2 cells (2.0
-rays was investigated in tobacco BY-2 cells and compared with that investigated in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO)-K1 cells as a reference. The resulting DNA fragments were separated by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and stained with SYBR Green I. Initial DSB yield was then quantified from the fraction of DNA fragments shorter than 1.6 Mbp based on the assumption of random distribution of DSBs. The DSB yield in tobacco BY-2 cells (2.0  0.1 DSBs Gbp
0.1 DSBs Gbp Gy
Gy ) was only one-third of that in CHO-K1 cells. Furthermore, the calculated number of DSBs per diploid cell irradiated with
) was only one-third of that in CHO-K1 cells. Furthermore, the calculated number of DSBs per diploid cell irradiated with  -rays of mean lethal dose was five times greater in tobacco BY-2 cells (263.2
-rays of mean lethal dose was five times greater in tobacco BY-2 cells (263.2  13.2) than in CHO-K1 cells. These results suggest that the radiation tolerance of tobacco BY-2 cells appears to be due to not only a lower induction of DNA damage but also a more efficient repair of the induced DNA damage.
13.2) than in CHO-K1 cells. These results suggest that the radiation tolerance of tobacco BY-2 cells appears to be due to not only a lower induction of DNA damage but also a more efficient repair of the induced DNA damage.
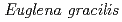
Hayashi, Hirotaka; Narumi, Issei; Wada, Seiichi; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Furuta, Masakazu*; Uehara, Kaku*; Watanabe, Hiroshi*
Journal of Plant Physiology, 161(10), p.1101 - 1106, 2004/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:23.18(Plant Sciences)The resistance of 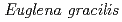 strains Z (wild type) and SM-ZK (chloroplast-deficient mutant) to ionizing radiation was investigated. The colony forming ability of
strains Z (wild type) and SM-ZK (chloroplast-deficient mutant) to ionizing radiation was investigated. The colony forming ability of 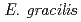 strain Z was higher than that of strain SM-ZK after
strain Z was higher than that of strain SM-ZK after  -irradiation. For both strains, the resistance of light-grown cells was higher than that of dark-grown cells, suggesting that the light conditions during the culture contribute to the radiation resistance of
-irradiation. For both strains, the resistance of light-grown cells was higher than that of dark-grown cells, suggesting that the light conditions during the culture contribute to the radiation resistance of 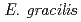 . The comet assay showed that the ability of rejoining DNA double-strand breaks (dsb) was much higher in the light-grown cells. These results suggest that
. The comet assay showed that the ability of rejoining DNA double-strand breaks (dsb) was much higher in the light-grown cells. These results suggest that 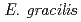 possesses a light-induced repair system to cope with DNA dsb.
possesses a light-induced repair system to cope with DNA dsb.
Ichige, Hisashi; Hiratsuka, Hajime; Honda, Masao; Miya, Naoyuki
Heisei-14-Nendo Tokyo Daigaku Sogo Gijutsu Kenkyukai Gijutsu Hokokushu, p.2_91 - 2_93, 2003/03
no abstracts in English
Zhao, Y. L.*; Nagame, Yuichiro; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sueki, Keisuke*; Nakahara, Hiromichi*; Goto, Shinichi*; Tanikawa, Masashi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(Suppl.3), p.30 - 33, 2002/11
no abstracts in English
Yamaoka, Hiroto*; Tsuchiya, Kazuyuki*; Awano, Toshihiko*; Oka, Kiyoshi
Ishikawajima Harima Giho, 42(5), p.260 - 264, 2002/09
no abstracts in English
Watanabe, Ritsuko; Saito, Kimiaki
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 41(3), p.207 - 215, 2002/08
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:51.29(Biology)no abstracts in English
Sakamoto, Fuminori; Suzuki, Eiji*; Fujii, Yuki*
Journal of Biochemical and Biophysical Methods, 52(2), p.97 - 109, 2002/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:9.68(Biochemical Research Methods)no abstracts in English
Zhao, Y. L.*; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Nagame, Yuichiro; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sueki, Keisuke*; Tanikawa, Masashi*; Goto, Shinichi*; Nakahara, Hiromichi*
Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemical Sciences, 3(1), p.103 - 107, 2002/06
no abstracts in English
Narumi, Issei; Sato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro
JAERI-Conf 2002-005, p.158 - 171, 2002/03
 is characterized by its extraordinary resistance to the lethal and mutagenic effects of ionizing and ultraviolet irradiations and many other DNA-damaging agents. By analyzing a DNA repair-deficient mutant strain, we discovered that a novel protein participates in the extreme radiation resistance of
is characterized by its extraordinary resistance to the lethal and mutagenic effects of ionizing and ultraviolet irradiations and many other DNA-damaging agents. By analyzing a DNA repair-deficient mutant strain, we discovered that a novel protein participates in the extreme radiation resistance of  . The protein (designated PprA for promoting prominent repair) can recognize DNA strand breaks. Further, PprA would protect irradiation-damaged DNA from exonuclease activity and consequent degradation and thereby ensure DNA repair processes could function. Beside DNA-binding ability, PprA can promote the activities of DNA ligase and RecA, suggesting that PprA functions as a DNA repair-promoting protein to potentiate the effectiveness of DNA repair. These properties enable PprA to use the widespread application
. The protein (designated PprA for promoting prominent repair) can recognize DNA strand breaks. Further, PprA would protect irradiation-damaged DNA from exonuclease activity and consequent degradation and thereby ensure DNA repair processes could function. Beside DNA-binding ability, PprA can promote the activities of DNA ligase and RecA, suggesting that PprA functions as a DNA repair-promoting protein to potentiate the effectiveness of DNA repair. These properties enable PprA to use the widespread application  and
and  .
.
Ito, Masayuki*
Nihon Gomu Kyokai-Shi, 75(2), p.68 - 72, 2002/02
no abstracts in English